Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Cystic fibrosis is a relatively rare, inherited disease that affects the lungs and digestive system. It is a disease that gets worse over time and will ultimately be fatal. It is estimated that there are about 30,000 people in the United States who are affected with CF and between 2,500 and 3,000 babies who are born with it each year. CF is most common in Caucasians who have a Northern European heredity but can occur in any race.
What is cystic fibrosis?
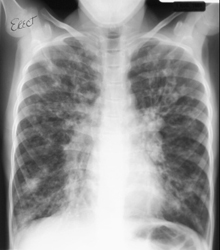
CF causes the glands that produce sweat and mucus to function abnormally, producing thick, sticky mucus. This mucus can clog the lungs causing serious breathing problems and lung disease. People with CF can also have problems with nutrition, digestion, growth, and development. There is no cure for cystic fibrosis and the disease generally gets worse over time. People with CF usually live into their mid-30s although new treatments are allowing people to live into their 40s and longer.
Causes
Cystic Fibrosis is a genetic disease that is inherited from two parents who carry an abnormal gene. This gene does not affect the parents and until recently it was not possible to know that they were carriers until the child was diagnosed. CF is NOT contagious.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary from person to person and are not always obvious in childhood. Symptoms include frequent episodes of wheezing, persistent cough, diarrhea that does not go away, foul-smelling stools, salty-tasting skin, poor growth, and chronic sinus infection.
Treatment
There is no cure for CF. Usually a person is diagnosed during childhood, specifically before they are one. Doctors will come up with the best treatment options depending on the patient’s specific health problems. The treatments will usually include a combination of medication and home treatments. These home treatments can be difficult but will help the patient live a longer, healthier life.
Ways of keeping healthy include: eating the doctor recommended diet (usually nutritious and high in calories), keeping immunizations current, avoiding tobacco smoke, using airway-clearing techniques, seeing a doctor frequently and seeking care from a Cystic Fibrosis specialty center.